Do you struggle to put on weight? Despite efforts to eat more, you just can’t get those extra kilos on? This may sound surprising, but it is the challenging reality for a lot of athletes.
There are many sports where an athlete’s body composition can impact their performance. Depending on the sport, some athletes may want to become heavier and gain muscle to increase strength, power and stability, as well as reduce weight loss to prevent injury and illness. This is common in athletes like football players, powerlifters and wrestlers.
However, it can be quite challenging to put on and maintain muscle, especially with high activity loads in training and competition. So, we are here to give you some simple tips to aid in weight gain and maintenance.
But to understand the reasons for these strategies, it is important to have a bit of background knowledge.
Energy surplus
Eating more energy than you expend is essential for gaining weight. Not only to fuel everyday functioning and exercise, but to support muscle protein synthesis (muscle repair and growth). Several factors can play a significant role in determining how much of an energy surplus an athlete may require to increase weight, including current body composition, genetics and activity levels. Therefore, this amount will be highly variable across individuals, with some only requiring a small increase in energy consumption, while others may require a lot more to get results.
Adequate protein
During exercise, muscle tissues are broken down. Protein plays a key role in helping muscles grow and repair in response to the stress of exercise. Therefore, consuming adequate protein is essential to promote effective muscle protein synthesis, especially in those looking to increase muscle strength and size, in combination with resistance training. For active individuals, it is recommended that they consume between 1.6-2.2g/kg/day of protein.
Strategies
Below are some simple strategies you can use to optimise weight gain:
- Aim to eat regularly throughout the day, every 2-3 hours
- Aim to include a source of protein in each meal and most snacks
- Increase the energy density of a meal by adding fats, including
- Avocado
- Nuts and seeds
- Nut butter
- Butter
- Cream, ice cream
- Fuel adequately pre and post training
- Include some energy dense, nutrient poor foods that are low in fibre. This may be required to get additional ‘easy to consume’ calories in
- Below are some examples of ways you can easily increase the energy in your meals
Breakfast
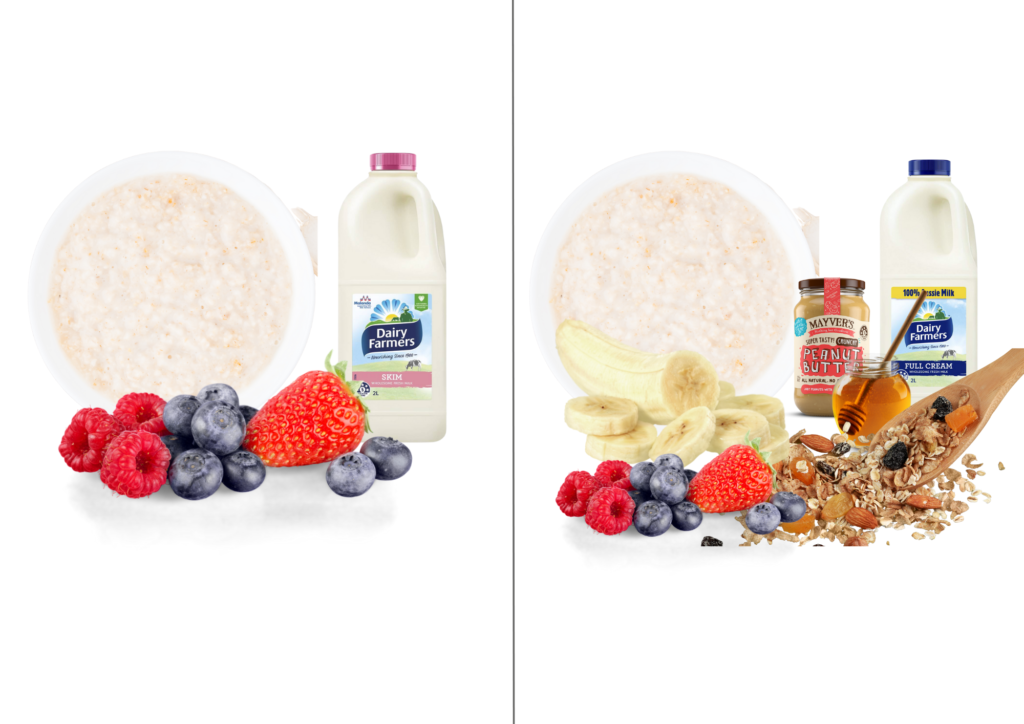

Strategies to increase energy density
- Use full fat milk
- Add nut butter and/or honey
- Top with nuts, seeds and/or granola
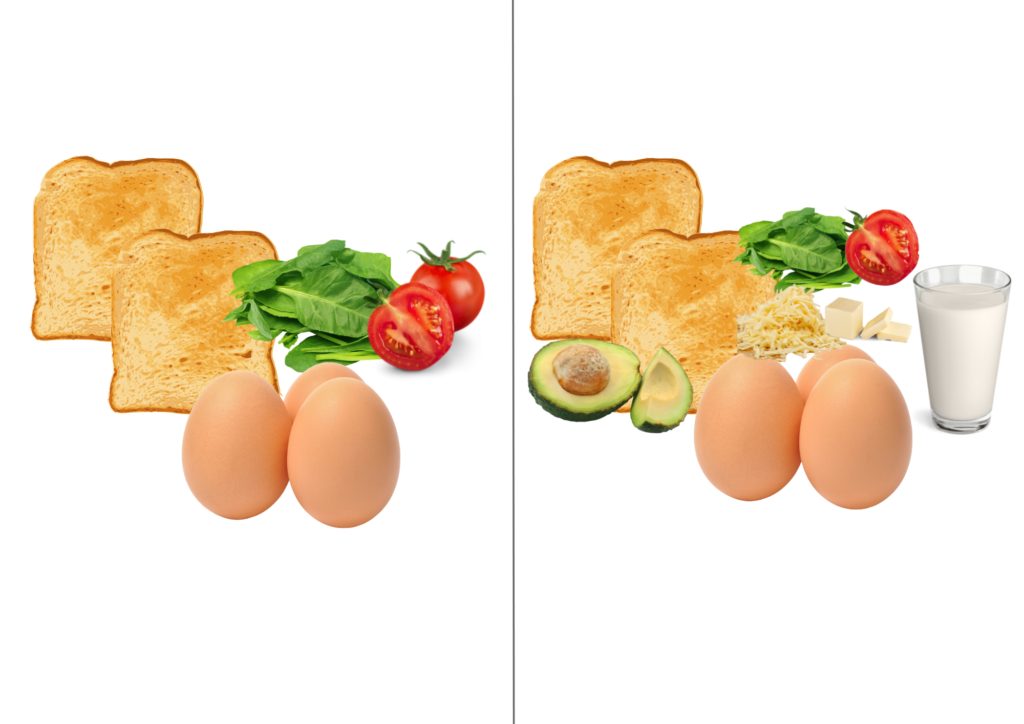
- Spread a thick layer of avocado on the toast
- Add butter or margarine and cheese to the eggs
Enjoy with a glass of milk
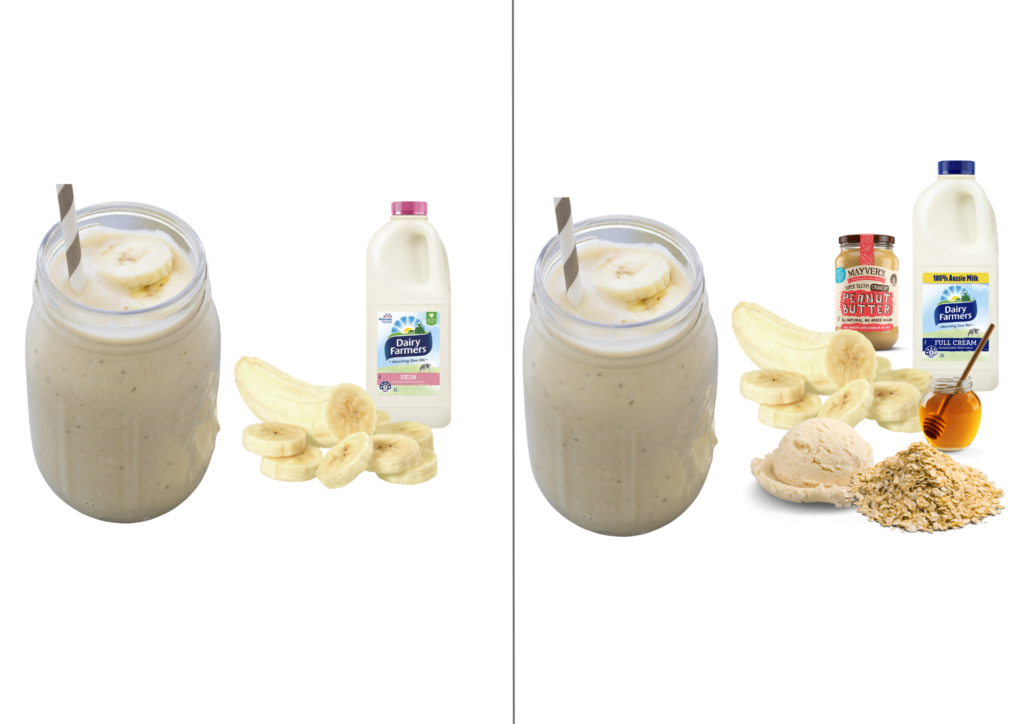

- Use full fat milk
- Add nut butter and/or honey
- Add Greek yoghurt or ice cream
- Add rolled oats or weetbix
Lunch
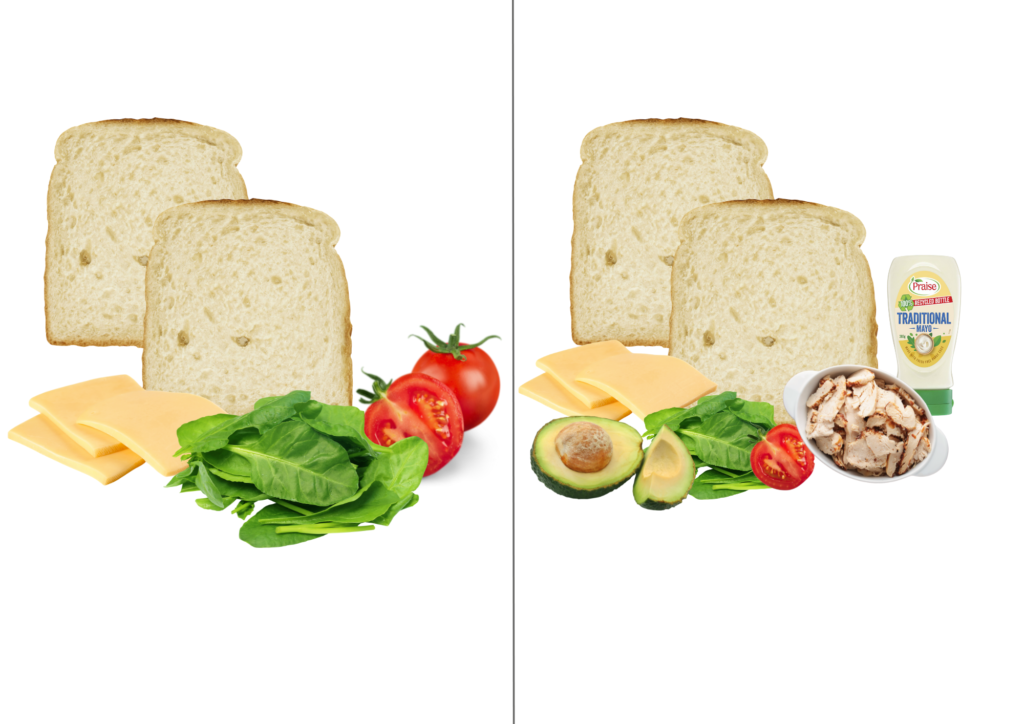

- Add protein rich fillings, eg egg, tuna, chicken, tuna
- Use a thick spread, eg avocado, mayonnaise, butter or margarine
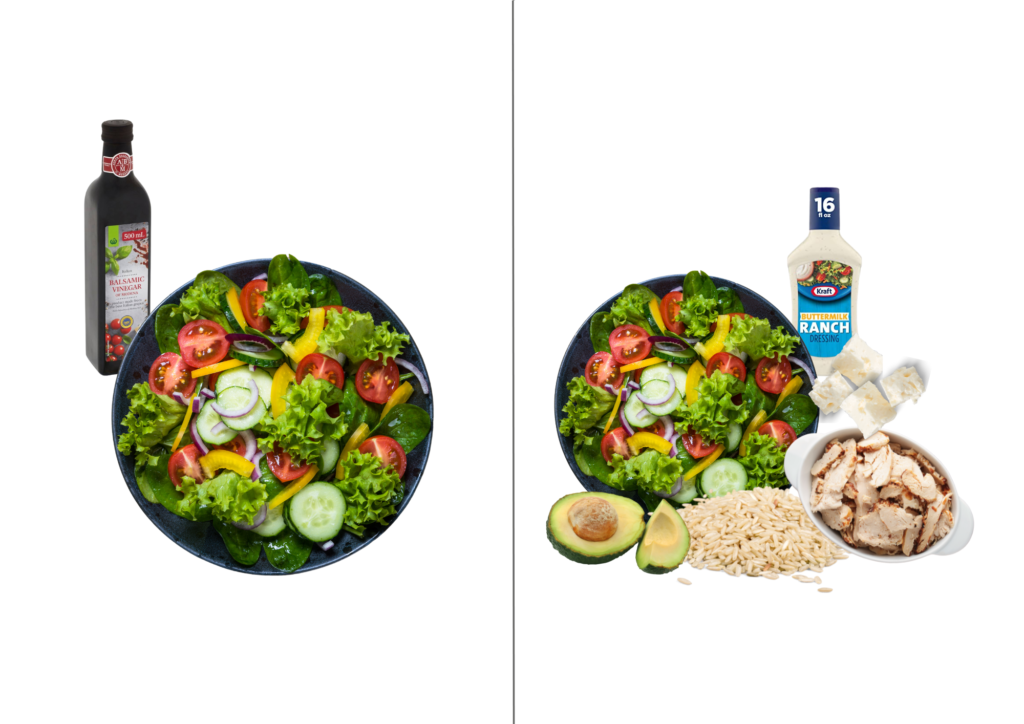

- Add a source of protein
- Add a source of carbohydrates
- Add a source of fat, eg avocado, nuts, seeds, a salad dressing, cheese
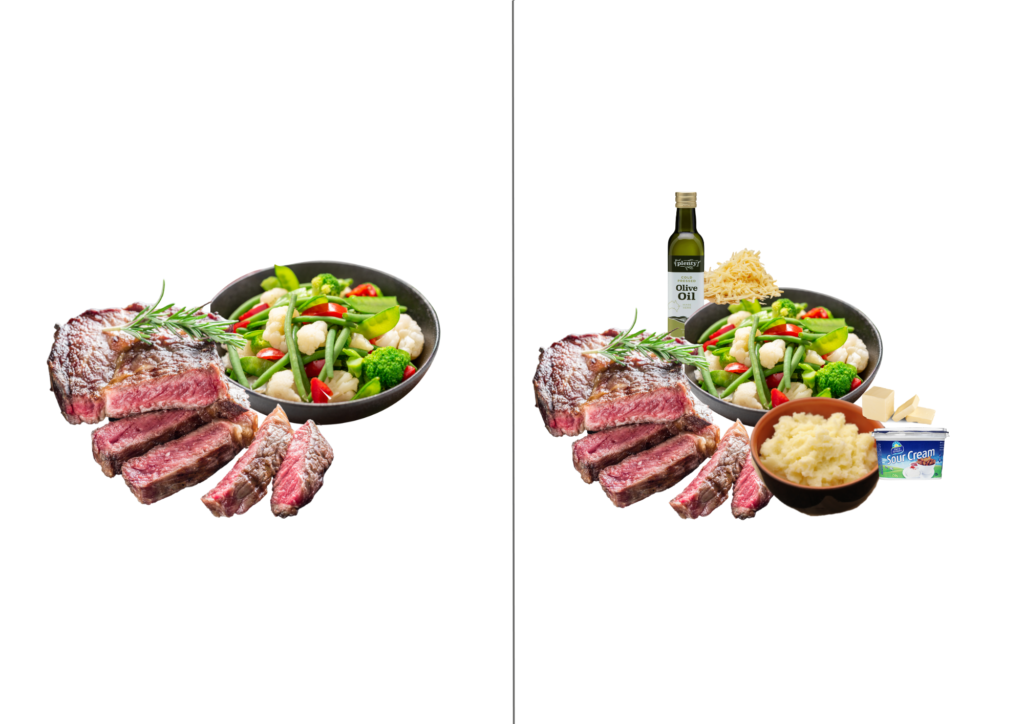

- Cook with extra virgin olive oil
- Add cheese to the vegetables
- Add milk, cream, butter or margarine to the mash potato
- Add a sauce or gravy
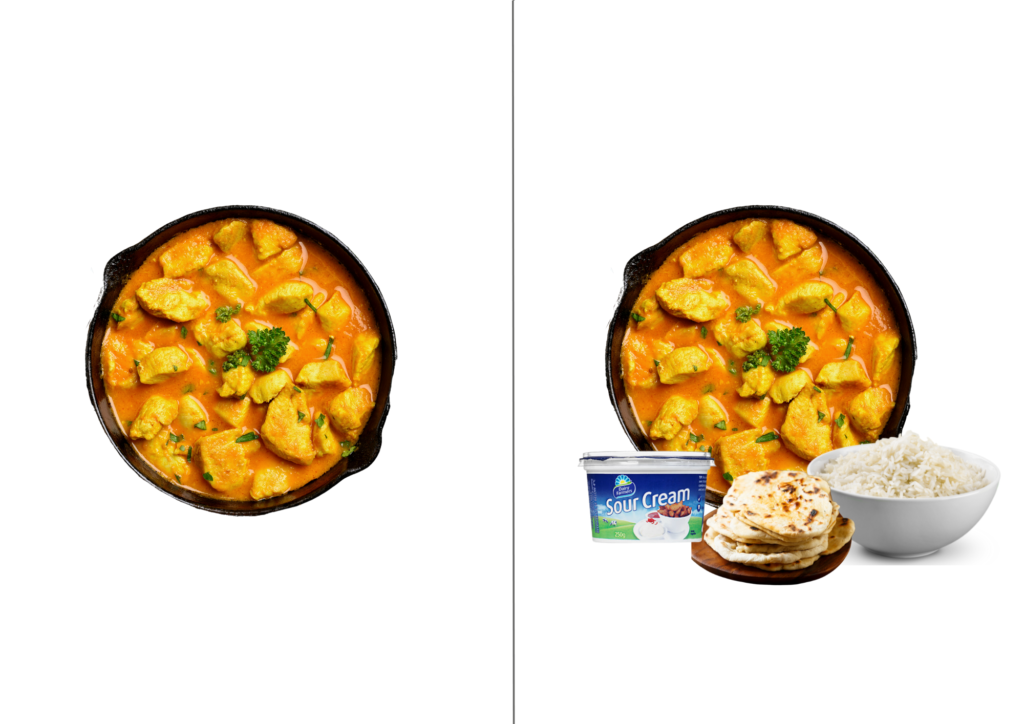

- Add a source of protein, eg beans, fish, beef, chicken
- Add cream or sour cream
- Serve with a source of carbohydrates, eg rice, potatoes, naan bread
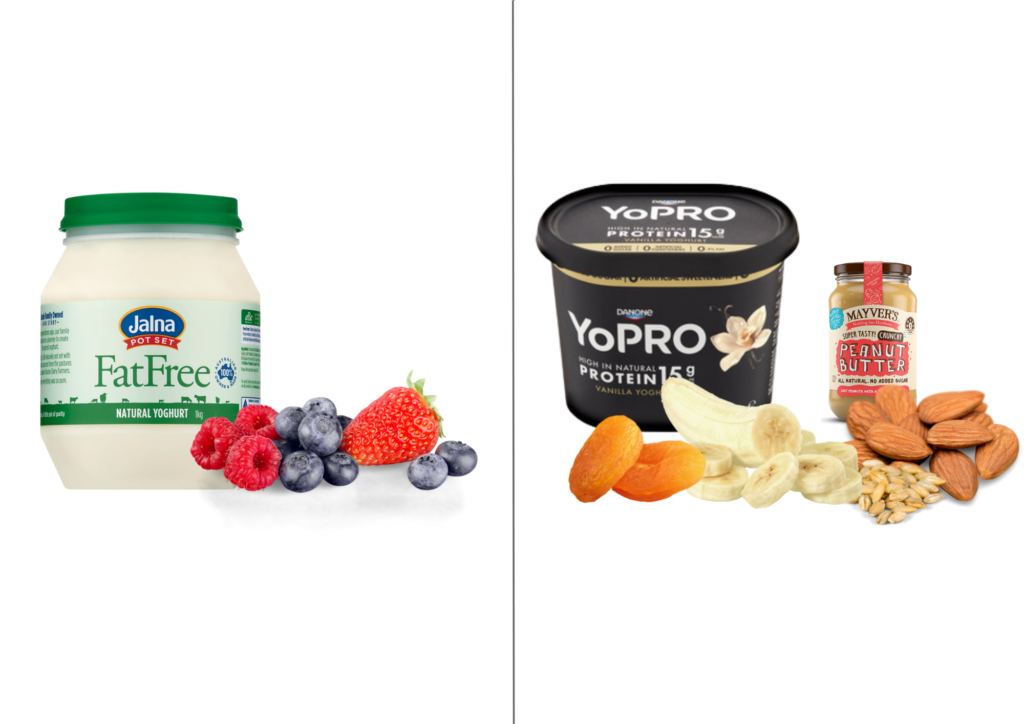

- Use full fat or high protein yoghurts
- Add dried and fresh fruit
- Add nuts, seeds and/or granola
- Add nut butter
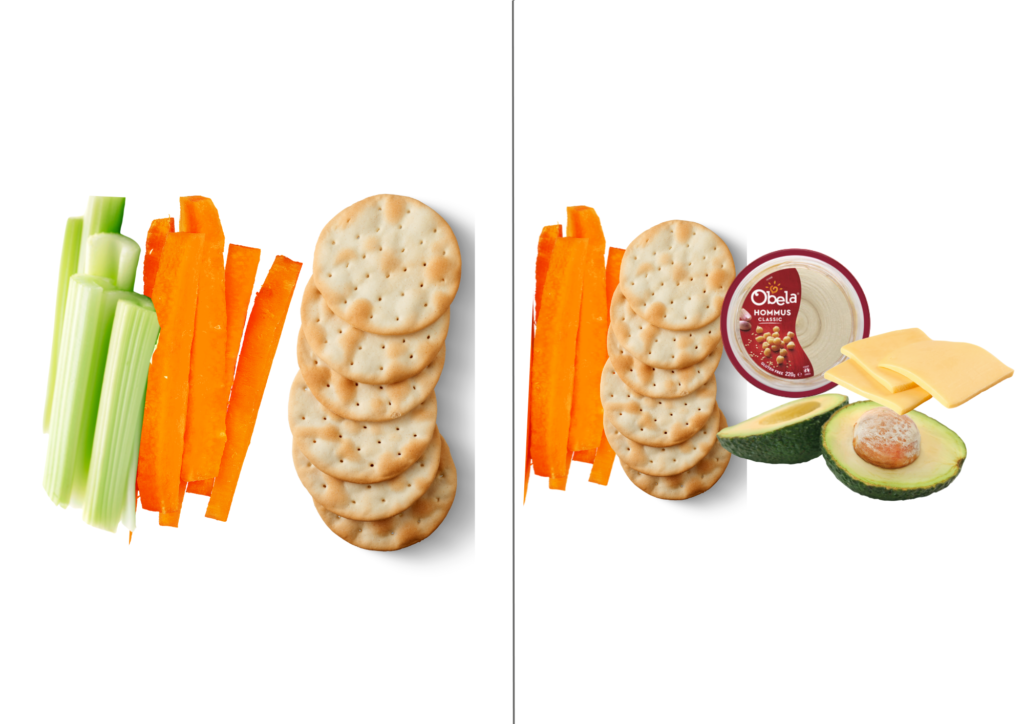

- Enjoy with avocado, cheese and bean based dips, eg hummus
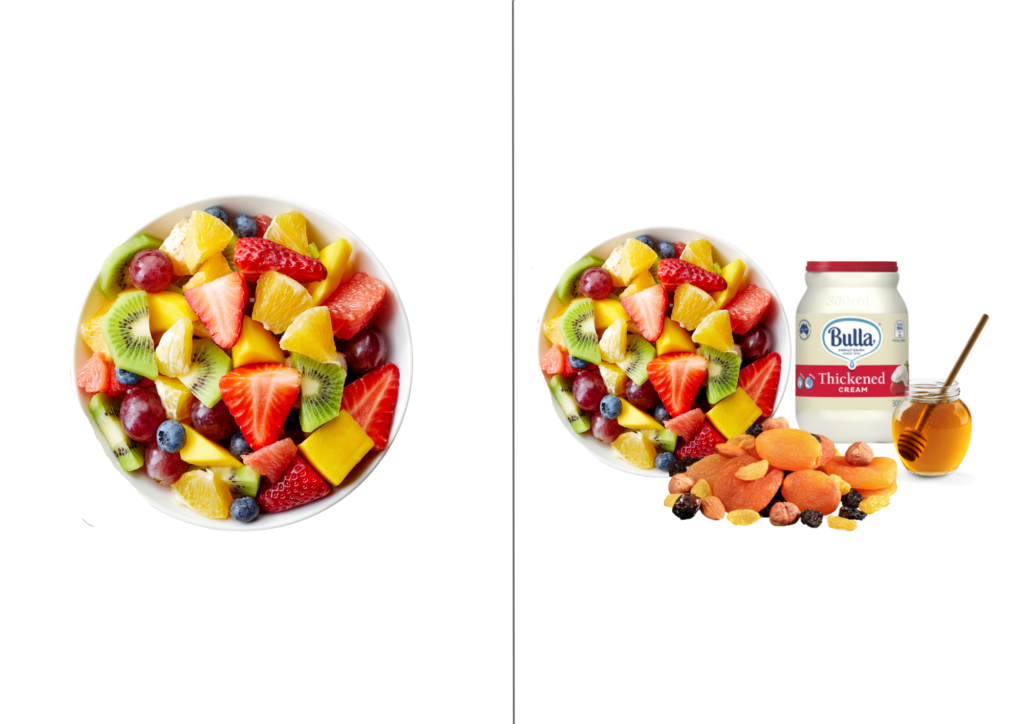

- Add dried fruits and nuts
- Top with yoghurt, cream, or cereal
- Add honey
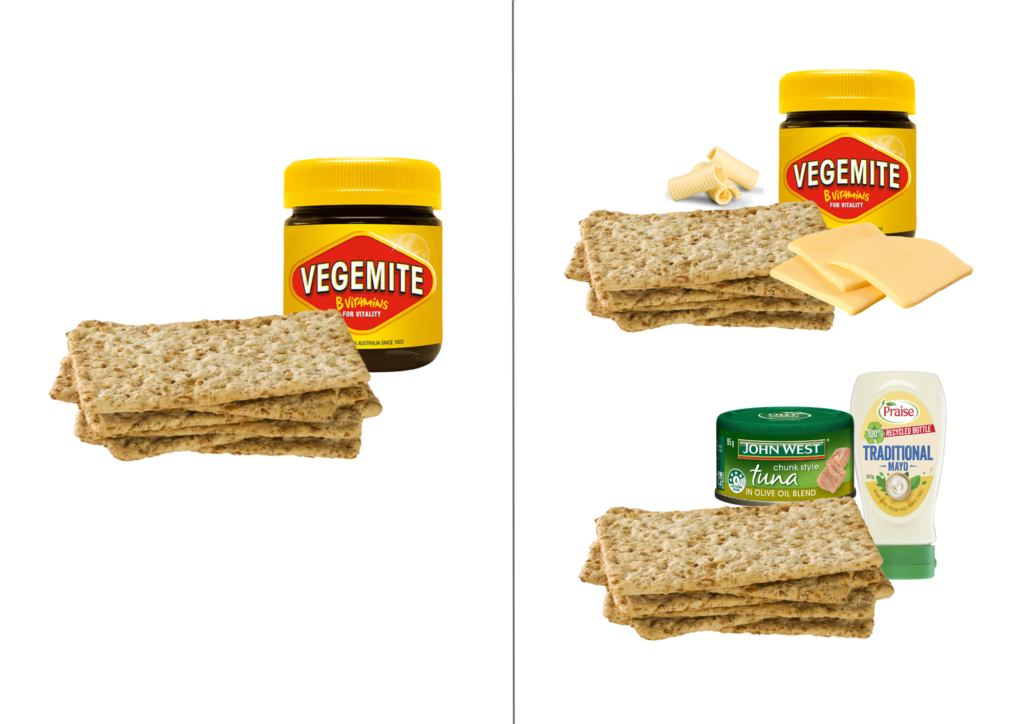

- Add cheese with margarine or butter, or
- Tuna and mayonnaise
Need individualised support to help you increase your muscle mass? Get in touch today to see how we can help.

